“Appendicitis: Serious repercussions may result from ignoring symptoms. Pay attention to your body; early intervention can save lives.”
Definition:
The inflammation of the appendix, a little pouch-like structure in the lower right belly, is the hallmark of the medical disorder appendicitis. Appendicitis can cause major, sometimes fatal consequences of a burst appendix if left untreated.
Here’s an overview of the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and complications of appendicitis:
1-Symptoms:
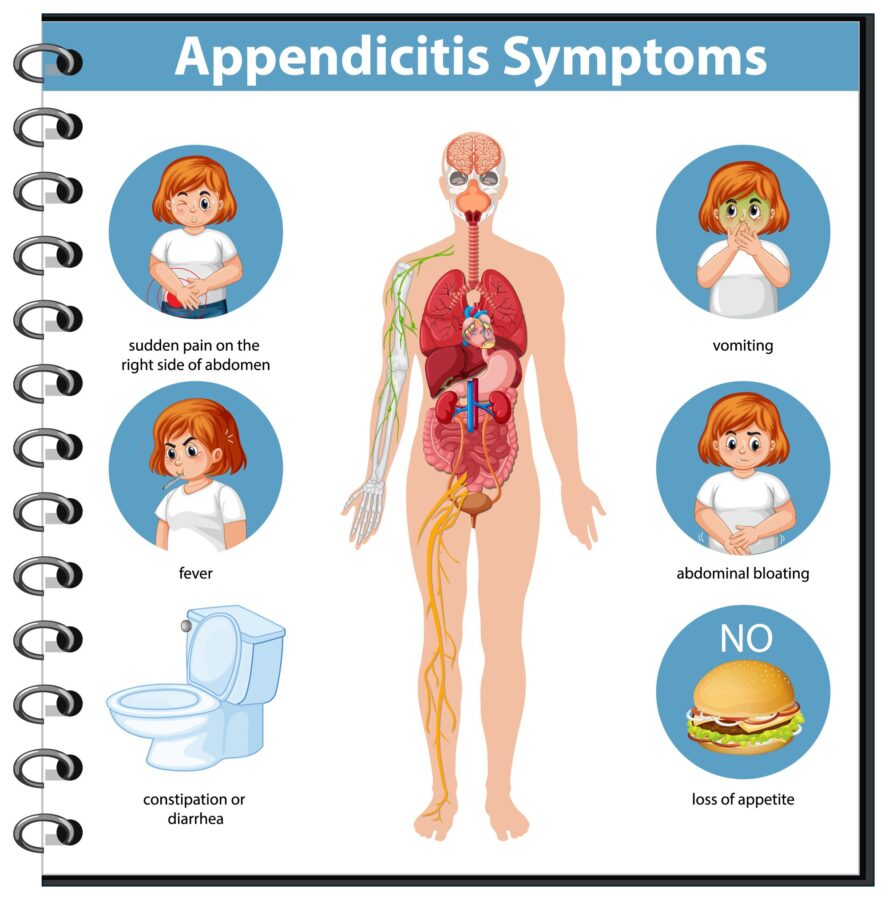
- Abdominal Pain
- Loss of Appetite
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Fever
- Diarrhea or Constipation
2-Diagnosis:
1-Physical Examination:
Physicians frequently do a physical examination to look for abdominal pain and indicators of peritonitis, or inflammation of the lining of the abdomen.
2-Blood Tests:
It is possible to perform blood tests to look for infection-related symptoms like an increased white blood cell count.
3-Imaging Tests:
One way to see the appendix and check for indications of inflammation or obstruction is to undergo imaging tests like an MRI, CT scan, or ultrasound.
3-Treatment:
1-Surgery (Appendectomy):
Surgery to remove the appendix is known as an appendectomy. For appendicitis, or inflammation of the appendix, this is the usual course of treatment. In order to stop the infected or inflamed appendix from rupturing and resulting in additional problems like peritonitis (infection of the abdominal lining), the surgeon removes it during the appendectomy.
There are two primary methods for doing this type of surgery, all of which require general anaesthesia. Open surgery requires a bigger abdominal incision, whereas laparoscopic surgery uses tiny incisions along with specialised instruments and a camera. The surgeon’s preference and the severity of the appendicitis are two criteria that influence the procedure choice. Following the operation, patients often heal rather quickly and are able to resume their normal condition.
2-Antibiotics:
In certain instances, especially when the diagnosis is unclear or surgery is postponed, a prescription for antibiotics may be issued to assist lower infection and inflammation.
4-Complications:
1-Ruptured Appendix (Perforated Appendicitis):
Prompt treatment of appendicitis is essential to prevent rupture of the appendix, which can introduce bacteria and infection into the abdominal cavity. A dangerous illness known as peritonitis may arise from this, necessitating prompt medical intervention.
2-Abscess:
An abscess, or pocket of pus, may occasionally develop around the appendix. This can call for another surgery or drainage using a catheter.
3-Bowel Obstruction:
An intestinal blockage may, in rare instances, result from scarring or inflammation following an earlier attack of appendicitis.
It is essential to diagnose and treat appendicitis as soon as possible to avoid complications. It’s critical that you get medical help as soon as possible if you think you or someone else may have appendicitis.
For more interesting blogs, visit: Wellnesio.com and blog page

👌😕