“Allergies are whispers from our bodies, urging us to listen closely, guiding us to a balanced coexistence with the world around us.”
INTRODUCTION:
Reactions of the immune system to typically harmless chemicals are known as allergies.
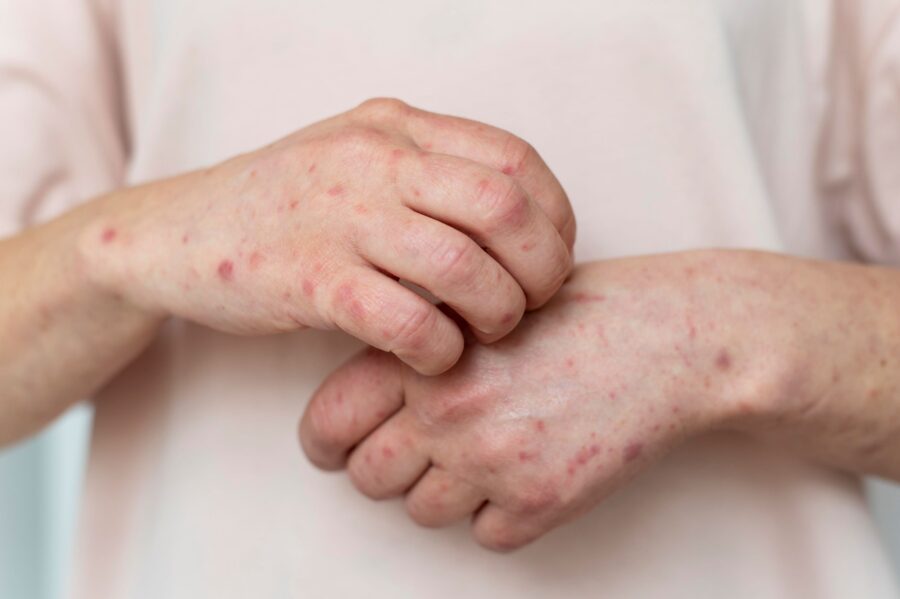
Allergens are substances that the immune system perceives as harmful and responds to by releasing compounds such as histamines. Allergy symptoms can range in severity from minor to severe and take many forms.
Types:
1-Respiratory Allergies:
- Hay Fever (Allergic Rhinitis): Caused by mould spores, dust mites, pollen, or pet dander.
- Asthma: Allergens such as pollen, pet dander, and environmental contaminants can cause inflammation of the airways.
2-Skin Allergies:
- Eczema (Dermatitis): Environmental variables, allergen exposure, or certain foods can all cause inflammation of the skin.
- Contact Dermatitis: Allergic reaction that occurs when certain metals, plants, or chemicals come into touch with the skin.
3-Food Allergies:
Nuts, eggs, milk, soy, wheat, fish, and shellfish are among the common allergies.
4-Insect Sting Allergies:
Bee, wasp, hornet, or ant stings can cause anything from minor swelling to life-threatening anaphylaxis.
5-Drug Allergies:
Allergy symptoms may arise from medication-related adverse reactions.
Symptoms:
1-Respiratory Allergies:
Breathing difficulties, coughing, wheezing, runny or stuffy nose, and sneezing.
2-Skin Allergies:
Rash, hives, redness, swelling, and itching.
3-Food Allergies;
Breathing difficulties, diarrhoea, vomiting, rashes, swelling, and itching.
4-Insect Sting Allergies:
Breathing difficulties, hives, swelling at the sting site, and itching.
5-Drug Allergies:
Respiratory symptoms, skin rash, oedema, itching, and in extreme situations, anaphylaxis.
Diagnosis:
Working closely with healthcare providers is essential for those with allergies to ensure correct diagnosis and management. Being aware of the potential consequences of allergic responses is essential, as they can range from minor annoyances to serious emergencies.
Allergy diagnosis usually entails a combination of physical examination, particular tests, and medical history assessment. This is a summary of the allergy diagnosing procedure:
1-Medical History:
- Thorough explanation of the signs, how often they occur, and possible causes.
- Identification of patterns, such as seasonal or environmental correlations.
2-Physical Examination:
- Examination of the respiratory system, skin, and other afflicted areas.
- keeping an eye out for any outward symptoms of an allergic reaction, such rashes on the skin or stuffiness in the nose.
3-Allergy Testing:
- Skin Prick Test: Common allergens in small doses pricked into the skin to see how the skin reacts.
- Blood Tests: Analyse certain antibodies (IgE) to determine the sensitivity to allergies.
- Patch Testing: Applied to the skin in dermatitis instances to determine contact allergens.
4-Elimination Diet;
- Removing probable allergens from the diet for a short while in order to track symptom improvement.
- Reintroducing foods one at a time to identify particular triggers.
5-Challenge Tests:
- Introducing suspected allergens under medical supervision in order to track and validate reactions is a common diagnostic procedure for food allergies.
6-Nasal Smear or Swab:
- Checking for eosinophils in nasal secretions, as they may be a sign of allergic rhinitis.
7-Lung Function Tests:
- Asthma diagnosis relies on spirometry, which evaluates lung function.
8-X-rays or Imaging:
- Imaging can sometimes be used to evaluate how allergens affect the respiratory system.
9-Medical Diary:
- A thorough record of symptoms, possible causes, and surrounding circumstances might help with diagnosis.
Treatment:
The kind and intensity of an allergic reaction determine how to treat it. Here are a few typical methods:
1-Avoidance:
Steer clear of the allergen triggering the reaction for the easiest approach to managing allergies. For instance, if you have a pollen allergy, remaining inside during the times when pollen counts are highest will help lessen symptoms.
2-Medications:
- Antihistamines
- Decongestants
- Nasal corticosteroids
- Allergy shots (immunotherapy)
3-Natural remedies:
Some people use herbal supplements, acupuncture, and other alternative therapies—like saline nasal rinses—to treat their allergies naturally. Though their efficacy and safety can differ, it is imperative to examine these choices with a healthcare expert prior to attempting them.
4-Consultation with an allergist:
Consult an allergist or immunologist if allergies are really impairing your quality of life or if your symptoms are very bad. They can do allergy testing to pinpoint certain triggers and suggest suitable courses of action.
Before beginning any new treatment plan, always get medical advice, especially if you’re thinking about mixing various drugs or therapies.
For more interesting blogs, visit: Wellnesio.com and blog page


Good Job❤