“Acne is a chapter, not the whole story. Acne teaches us that true beauty lies not in perfection, but in the strength to embrace & heal imperfections.”
What is acne?
Acne is the growth of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, cysts, or nodules on the skin. It usually happens when dead skin cells and grease clog hair follicles. Often, acne affects the face, neck, shoulders, chest, and back.
- Face: Effects almost everyone
- Back: Effects more than 50%
- Chest: About 15%
Types Of Acne:
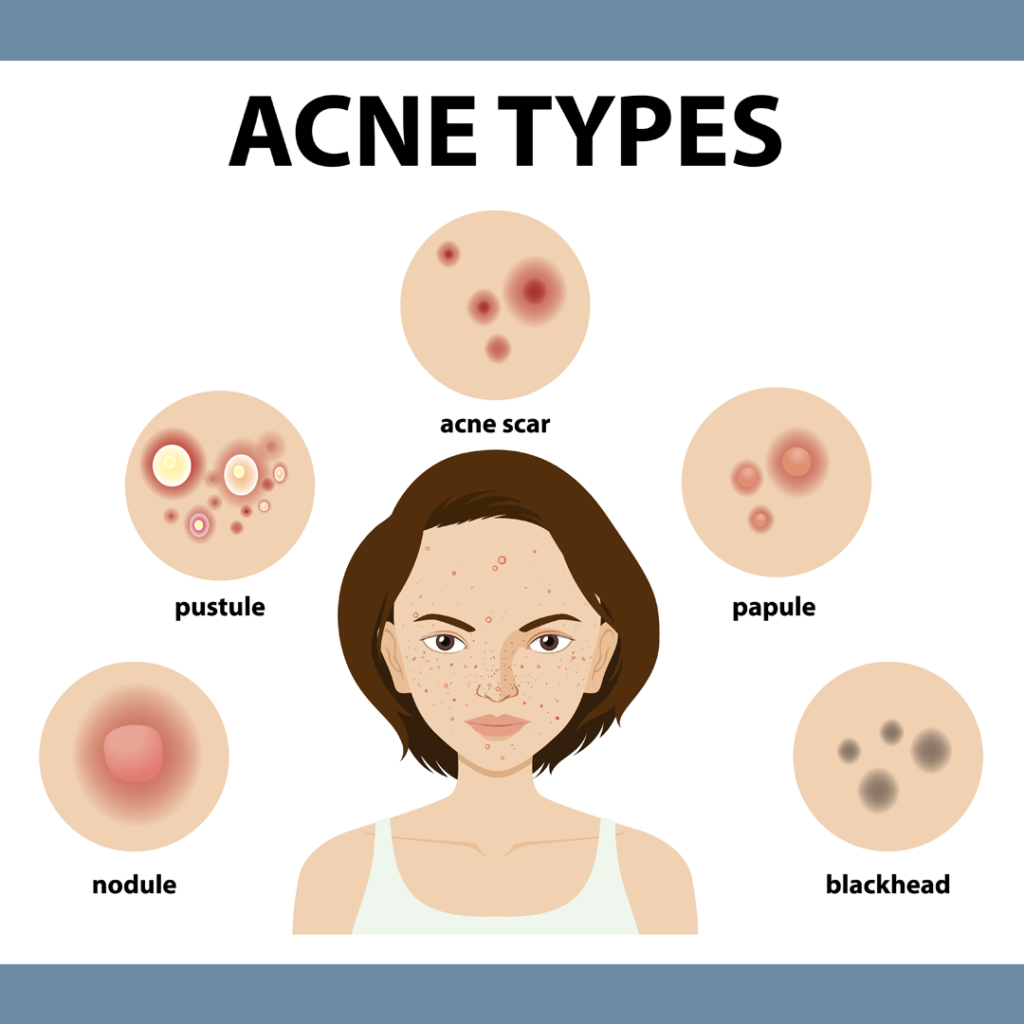
1-Whiteheads:
- Appearance: Small, round, or oval-shaped bumps with a white or flesh-coloured top.
- Texture: Closed comedones with a thin layer of skin covering the clogged pore.
- Location: Typically found on the face, especially in areas with a higher concentration of oil glands, such as the forehead, nose, and chin.
2-Blackheads:
- Appearance: Small, dark or black-coloured bumps with an open pore at the centre.
- Texture: Open comedones with a visible black or dark brown plug at the surface.
- Location: Commonly found on the face, particularly in areas with a higher concentration of oil glands, such as the nose, forehead, and chin.
3-Papules:
- Appearance: Small, red or pink bumps with a raised surface.
- Texture: Solid, without a visible centre or any fluid-filled area.
- Tenderness: Papules are often tender to the touch and can be painful.
4-Pustules:
- Appearance: Small, round bumps with a white or yellow centre of pus.
- Texture: Inflamed and tender to the touch.
- Colour: The surrounding area is often red, giving the pustule a noticeable appearance.
5-Nodules:
- Appearance: Large, solid, often painful bumps beneath the skin’s surface.
- Texture: Solid and firm to the touch.
- Pain: Nodules are usually tender and painful.
6-Cysts:
- Appearance: Large, fluid-filled, often painful lumps beneath the skin.
- Texture: Soft, fluctuant, and filled with pus.
- Pain: Cysts are typically tender and can be associated with throbbing pain.
Causes Of Acne:
1-Excess Oil Production:
Excess sebum secreted by the sebaceous glands.
2-Clogged Pores:
Accumulation of oil and dead skin cells, which clogs hair follicles.
3-Bacteria:
Inflammation can result from the Propionibacterium acnes (P. Acnes) bacteria growing in clogged pores.
4-Hormones:
Hormonal fluctuations can be the cause of acne, especially during adolescence, menstruation, and pregnancy.
5-Genetics:
Acne in the family may make someone more susceptible.
6-Certain Medications:
Certain medications, like contraceptives and corticosteroids, may exacerbate acne.
Diagnosis Of Acne:
1-Clinical Examination:
When examining a patient’s skin, a dermatologist looks for lesions that are typical of acne, such as papules, pustules, cysts, whiteheads, and blackheads. The diagnosis takes into account the location and extent of lesions, as well as any indications of inflammation or scarring.
2-Medical History:
The medical professional talks about the patient’s past and present skin issues, prescription drugs, lifestyle choices, and family history of acne. Relevant information may include details regarding hormonal changes like adolescence, menstruation, or pregnancy.
3-Discussion of Symptoms:
The patient answers questions on any discomfort, pain, itching, or tenderness related to the acne lesions.
4-Differential Diagnosis:
To achieve an accurate diagnosis, the medical expert may take into account other skin disorders including rosacea, folliculitis, or perioral dermatitis that may mimic acne.
5-Additional Tests (if necessary):
A clinical examination and medical history are usually sufficient to make a diagnosis. Still, other tests or examinations can be required in specific circumstances. To rule out underlying illnesses or infections, these could include skin biopsies, skin cultures, or blood testing.
Treatment Of Acne:
1-Topical Treatments:
Over-the-counter or prescription creams, gels, or lotions containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids.
- Benzoyl peroxide: Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial properties.
- Salicylic acid: Chemical exfoliant with anti-inflammatory properties.
- Retinoids: Stimulates collagen production, a protein that provides structure and firmness to skin.
2-Oral Medications:
Antibiotics, oral contraceptives, or isotretinoin may be prescribed for more severe cases.
- Topical antibiotics: Clindamycin, Erythromycin
- Oral antibiotics: Doxycycline, Minocycline, Tetracyclines
- Isotretinoin: Derivative of vitamin A with anti-inflammatory & antibacterial properties
3-Procedures:
Dermatological procedures like chemical peels, laser therapy, or drainage and extraction for cysts.
- Chemical peel: Involves the application of chemical solution to the skin to exfoliate the top layers.
- Laser therapy: Uses focus light to treat various skin conditions to reduce acne causing bacteria and inflammation.
Prevention:

1-Regular Cleansing:
Skincare that is gentle in order to prevent clogged pores and eliminate excess oil.
2-Avoiding Touching or Picking:
Scarring can result from picking at acne lesions or touching the face, which can exacerbate inflammation.
3-Proper Skincare:
Use moisturisers and skincare products that are non-comedogenic.
4-Balanced Diet:
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may help shield the body against developing acne.
5-Hydration:
Keep your skin hydrated by drinking lots of water.
6-Stress Management:
Stress can worsen acne, therefore practising stress reduction techniques might be helpful.
It’s essential to consult with a dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment options based on the severity and type of acne.
For more interesting blogs, visit: Wellnesio.com and blog page


That’s really Good😄